Ent vignettes |
|
- Hearing Loss
- Identifying Deafness in Very Young Children
- Cochlear Implants
- Ear Aches
- Discharging Ear
- Sudden Hearing Loss
- Vertigo Diagnosis And Management
- Sino Nasal Polyposis
- Epistaxis Management
- Allergic Rhinitis
- Obstructive Sleep Apnoea And Snoring
- Foreign Body
|
|
1. Hearing Loss
Types of hearing aids
- Body worn
- Behind the ear (BTE)
- In the canal (ITC)
- Completely in the canal (CIC)
- Programmable
- Digitally programmable
- Bone anchored hearing aids (BAHA)
Canal hearing aids

- For patients with loss 40-60 db HL
- Can be used with lower gain
- No occlusion effect
- No feedback- can use telephone normally
- Cosmetic appeal
Programmable hearing aids
- For patients with loss 30-100 db HL
- Better Speech reception at programmed frequencies
- Feedback manager
- No distortion
Digitally programmable hearing aids
 
- For patients with loss 30-80 db HL
- Better Speech reception
- Suppresses environmental noise for better clarity
- Feedback manager
|
top |
2. IDENTIFYING DEAFNESS IN VERY YOUNG CHILDREN
- Loud Noise: Startle
- Recognises Parents Voice
- Parents voice soothes the child
- Child responds to envt. Sound
OAE-Immediately after birth

BERA-Confirmatory test at 3 months

Remedial measures
- Hearing Aids
- Cochlear Implants (When hearing aids are not enough)
top |
|
|
3. COCHLEAR IMPLANTS

What is a cochlear implant ?

Device for patients with profound SNHL who get no benefit from high powered hearing aids

Level of hearing loss

Selection Criteria for Implantation - Adult
- Little or no benefit from the use of hearing aids
- Severe to profound bilateral sensorineural hearing loss
- Aided speech perception is important in determining cochlear implant candidacy, since it is speech perception, not sound awareness, that
determines the ability of a hearing-impaired person to function.
Selection Criteria for Implantation
Audiological
Aided speech perception is the more important of the two measures in determining cochlear implant candidacy, since it is speech perception, not sound awareness, that determines the ability of a hearing-impaired person to function.
Selection Criteria for Implantation - Adult
Audiological
Severe to profound bilateral sensorineural hearing loss
Preoperative evaluation

- Decision for or against implantation is a team decision.
- Evaluations
- Medical otological evaluation
- Audiological evaluation
- Psycho-social evaluation
- Counseling / informed consent
Audiological evaluation
- To determine the level and site of the hearing impairment along the auditory system .
- Pure Tone Audiometry
- Aided Audiometry
- BERA, OAE.
- ASSR
Full hearing profile
Communication history
- Current communication mode
- Current communication need Amplification history
- History of hearing aid/ tactile aid/ other ALD use
- Present aid(s) and settings
- Past and present benefit
Medical Evaluation
- Ears free of infection
- Intact auditory nerve
- No contraindications for surgery
- No radiological contraindications to placing the implant in the cochlea and mastoid
No radiological contraindications
C.T. scan, 3-D MRI
The process of implantation involves…..
- Assessment, decision, and preparation
- Surgery (3 hours) & 3 days stay.
- Fitting and switch- on after 3 weeks.
- Rehabilitation, training and further re-programming for 1-2 yr in prelingual.
What We Expect from Patient!
- Support from family and friends
- Psychologically prepared and motivated
- Realistic expectations
- Other considerations: etc proximity to clinic, support services, financial resources
Result
Adult recommended for cochlear implantation should have
- A good chance of improved hearing using the implant
- A minimal chance of a reduction in auditory ability
Cochlear Implant Team
- Family
- Team Co-ordinator
- Surgeon
- Audiologist / Speech and Language trainer
- Teacher of the Deaf
- Family Counsellor / Psychologist
- Consultant Professionals : Paediatrician, Neuropsychologist, Radiologist, Psychologist, Occupational Therapist etc.
Implant in Situ
top |
|
4. EAR ACHES
Furuncle:

- pain followed by purulent ear discharge.
- aural hygiene, antibiotics,I-G packing,analgesics.
Cerumen Removal

Otomycosis

- blackish discharge in rainy season, accompanied by itching and ear ache.
- aural hygiene, anti fungal , antihistaminic , analgesic.
Otomycosis (treatment)
- Cleaning &removal of debris
- Syringing
- Suction
- Topical antifungal drops 7-14 days
- Analgesics & antibiotics
- Systemic Antifungals rarely reqd.
Malignant otitis externa
- persistent discharge in a diabetic patient associated with ear ache
- Diabetes control & Medical/Surgical T/t
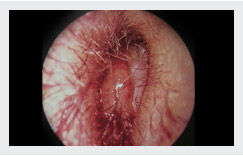 
ASOM

- Stage Of tubal occlusion
- Stage Of congestion
- Stage Of suppuration
- Stage Of resolution
- Stage Of complication
| top |
5. DISCHARGING EAR

Ear discharge:Color
  
- Green/yellow:pus:
- Otitis externa
- Otitis media
- Black/ ‘wet newspaper’: fungus
- Brown: wax
- Clear:CSF
CSOM
TUBO-TYMPANIC TYPE (SAFE)
   
CSOM unsafe
- scanty purulent discharge,foul smelling , blood stained
- Surgical T/t
 
Complications

- Extra Dural Abscess
- Sub Dural Abscess
- Meningitis
- Brain Abscess
- Sigmoid SinusThrombophlebitis
- Otitic Hydrocephalus
- Extracranial

- Facial paralysis
- Labyrinthitis
- Luc’s,Citelli’s,postaural abscess
INVESTIGATIONS
Pure Tone Audiometry
X-Ray Mastoid
Towne’s view
Stenver’s view
Ear microscopy
Hb%,TLC,DLC,ESR,Platelet count,PT,APTT,Urine R/M
TREATMENT
- ASOM
- Antibiotics,decongestants,ear Toilet
- myringotomy
- CSOM
- Antibiotic ear drops,ear toilet
- TT: Tympanoplasty
- AA: Mastoidectomy &Tympanoplasty
SURGERY

- Myringoplasty: repair of TM
- Tympanoplasty I: repair of TM & inspection of ossicles & ME
- Tympanoplasty II & III:Repair of TM & ossicles
- Modified Radical Mastoidectomy :
- Canal Wall Down procedure in which disease is cleared completely > safe dry ear & hearing is preserved
- Radical Mastoidectomy:
- Canal wall down procedure in which disease is exteriorized & hearing is not reconstructed
GOALS OF SURGERY
- Safe Dry Ear
- Closure of perforation
- Hearing Improvement
| top |
6. SUDDEN HEARING LOSS
-
An ENT Emergency
- A little alertness and prompt action can save you from permanent deafness!
- The cause could probobly be due to impairment of vascular supply to the inner ear or a post viral etiology
Management of Sudden Hearing loss
- If revived within first 24-48 hours you may be saved from permanent hearing loss.
- Immediate corrective measures like:
- Steroid therapy
- Drugs to improve circulation
- Hyperbaric Oxygen therapy
May help to save the inner ear.
Contact your ENT Surgeon immediately
| top |
7. VERTIGO DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
Introduction
- common complaint
- the cause often remains undetermined
- lack of a shared vocabulary
- not confined to any particular medical specialty.
- Physician
- Cardiologist
- Neurologist
- Orthopedician
- Otolaryngologist
Basic Physiology

Role of a family physician
- to evaluate dizzy patients
- identify serious problems
- identify treatable conditions
- when to ask for special tests
- when to refer
History in Vertiginous Patients
The history helps to establish
- Whether the subject does have a balance disorder.
- peripheral / central in origin.
- probable etiology?
History
CNS symptoms
- blurred vision
- diplopia
- dysarthria
- incontinence
- motor or sensory deficit
- gait disturbances
Indicate central pathology
Physio-therapy
- Counselling & mental assurance
- Cawthornes Head & Neck Exercises
- Body exercises
Treatment
- Treatment depends on the etiology and should include removal of the cause of symptoms if identified.
- Ear infection (bacterial or viral)
- Meniere’s disease
- Stroke
- Multiple sclerosis
- Acoustic neuroma
- Head injury
- Cervical Spondyosis
Conclusion
- Diagnosis of the cause of vertigo is a challenging problem and often requires a multi disciplinary approach.
- Inspite of sophisticated investigations often exact diagnosis is made in 40-50%pts. May not be arrived at in rest.
- Clinician treats the patient on medicines & physiotherapy.
- Symptomatically improve and follow up.
| top |
8. SINO NASAL POLYPOSIS
Associations
- Asthma
- Asprin Intolerance
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- Allergic Rhinosinusitis
Pathophysiology
- Environmental
- Genetic
- Proinflammatory Cytokines
Clinical Presentation
- Nasal Congestion
- Watering of eyes
- Rhinorrhoea
- Heavy Headedness
- Olfactory Dysfunction
Treatment
- Intranasal Corticosteroids
- Fluticasone-Azelastine Spray
- Medication-Anti-allergics
- teroids
- SURGERY-POLYPECTOMY
- FESS or MESS
| top |
9. EPISTAXIS MANAGEMENT

| top |
|
10. ALLERGIC RHINITIS
Statistics
- Affects upto 20% of adult population.
- 4 billion Rs.spent annually on visits & Tt.
Epidemiology
- Most Frequently in adolescents & young adults
- Males = females
- Chances of child suffering from AR:
- 29% - if one parent has AR
- 47% - if both parents have AR
- 80% of asthmatics have AR.
- 40% of AR patients have asthma.
Pathophysiology
Sensitization of Nasal Mucosa to Allergen
- Subsequent Exposure
- IgE cross linkage on Mast cells.
- Degranulation
- Release of Inflammatory Mediators
- Allergic Symptoms
Allergens
| Indoor Allergens |
Outdoor Allergens |
- Dust mites
- Animal Dander's
- Cockroaches
- Molds
|
- Pollens
- Paints
- Plastics
- Latex Gloves
|
Clinical Presentation
- Itching
- Rhinorrhoea
- Sneezing
- Ocular Pruritis
- Tearing
- Pharyngeal Itching
- Dry Cough
Examination
- Anterior Rhinoscopy
- Pale, boggy mucosa
- Hypertrophied turbinates
- Thin & clear or thick nasal secretions
- Decongestion of mucosa for further evaluation
- Endoscopic Nasal Examination.
Specific Investigation
- Allergen Identification
- Skin Testing with Allergen Extracts
- Measurement of Antigen Specific IgE Antibodies in serum.
Therapy
- Prevention remains the mainstay.
- Pharmacotherapy:
- Topical Intranasal corticosteroid sprays are the mainstay of pharmacotherapy
- H1 Antihistaminics preferably Non-sedating type
- Decongestants
- Cromolyn Sodium
- Immunotherapy
Novel Therapies
- Anti – IgE therapies.
- Immunotherapy using immuno-stimulatory DNA Sequences, Cytokines & Bacterial products.
| top |
11. OBSTRUCTIVE SLEEP APNOEA AND SNORING
Noise generated by the vibration of soft floppy parts of base of tongue, soft palate, uvula and surrounding pharyngeal tissue due to narrowing of airways.
Prevalence of Snoring and OSA
- 30 – 40% of the population has snoring
- 6 – 8% of the population has OSA
- Causes of Sleep Apnea
- Cranio-Facial Anomalies
- Short Stubby Neck
- Long Narrow Face
- Tapering Lower Jaw
- Retroposition of the Mandible
- Micrognathia
- Hyoid Bone More Inferiorly Positioned
- Longer and Flabbier Soft Palate
- Macroglossia
Signs and Symptoms of OSA
- Snoring
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness
- Excessive Fatigue
- Irritability
- Anxiousness
- Depression
- Poor Memory
- Poor Concentration
System for Grading the Size of the Oral Aperture

Normal Oropharynx

Obstructed Oropharynx

Conservative Management
The treatment of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea includes a variety of interventions. Weight loss is generally recommended. In addition, there are a variety of nasal and oral airflow devices, including CPAP, BI-PAP masks to reduce obstruction during sleep.
Volumetric Reduction of Palate by Radiofrequency Probe

Volumetric Reduction of Base of Tongue


| top |
12. FOREIGN BODY
- Ear
- Nose
- Bronchus
- Esophagus
Method of Nasal Foreign Body Removal
- Reassurance to patient and his / her attendant
- Hold the patient in mother’s / father’s lap or wrap in towel
- Spray with 10% Xylocaine or 4% Xylocaine with 2 Ampoules of adrenaline
- Suction of nasal cavity & visualize foreign body
- Use Eustachian Tube catheter or nasal packing forceps to remove
- Check for bleeding
- Pack with nasal tampoons

Recent Advances in Otorhinolaryngology
Endoscopicsurgery
- Equipments
- Light Source
- Fibreoptic Cord
- Telescopes 00 ,300 , 450 , 900 , 1200
- CCD Cameras 1/3 Chip&Monitor
- Surgical Instruments
- Hand Held
- Powered-Debrider
Endoscopic Surgeries
- Sinus Surgeries
- CSF Rhinorrhoea
- Optic Nerve Decompression
- Dacryocystorhinostomy
- Hypophysectomy
- Angiofibroma, Ben.Tumours
- Chonal Atresias
Lasers
Definition-Light Amplified Stimulation of Emitted Radiation
Types of Lasers
- CO2 Laser
- Argon Laser
- KTP Laser
- Nd-YAG Laser
Mode of action
- Beam reaches target cells
- Generates heat within the cells
- Steam is formed –rupture ofcells
- Fume generated-plume
- Lesion evaporates
Instruments
- Laser Source
- Aiming Beam
- Hand Piece(For delivering laser)
- Protective Devices
- Eye Goggles
- Eye Shilds
- Masks
- Special Endotracheal Tubes
Surgeries
- Tonsillectomy
- Turbinate Resection
- Stapedotomies
- Laryngeal Surgeries
- Papillomatosis
- Billateral TVC Abductory Palsy
- Leukoplakia
Powered instruments
MICRODEBRIDER (XOMED)
Parts of MICRODEBRIDER
- Micro Motor Source
- Direction
- Speed
- Cable
- Hand Piece
- Suction Cum Drill Port
- Irrigation Port
Surgeries
- Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
- (Especially nasal polyposis)
- Laryngeal Surgeries
- (Example: Laryngeal polyp)
- Adenoidectomy
| top |
|
|
|
